World floods and droughts will intensify prior to anticipated, research present
[ad_1]
Report floods and droughts fuelled by the El Niño and La Niña phenomena across the globe, from Australia to west Africa and the US to Argentina, are anticipated to develop into additional intensified by local weather change by 2030, in keeping with the most recent scientific stories.
A brand new research printed in Nature concluded that the affect of a warming planet in pushing up ocean temperatures within the japanese Pacific might be detectable within the climate patterns in eight years — nearly 70 years sooner than beforehand thought.
The La Niña phenomenon, which includes a large-scale cooling of the Pacific Ocean’s floor, drives modifications in wind and rainfall patterns world wide. Usually, the sample drives extra rain in components of Asia, together with Australia, and drier situations in components of the US, South America and Africa.
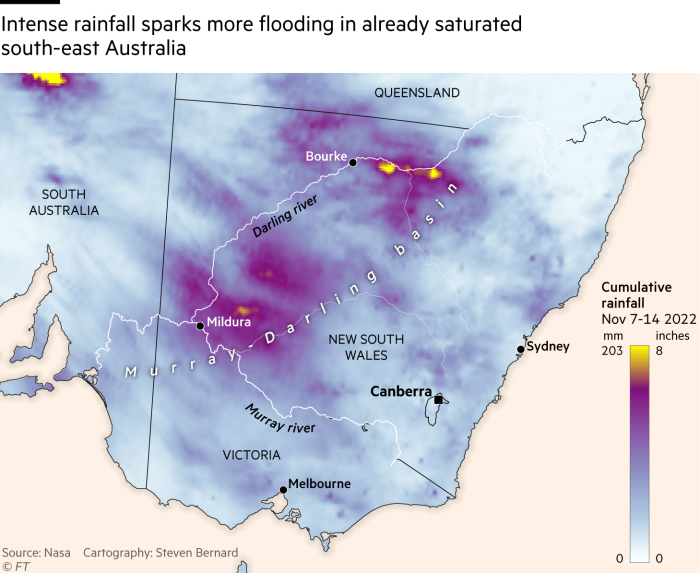
At current, the world is experiencing the primary “triple dip” La Niña climate sample in additional than 20 years, exacerbating patterns of flooding and drought in some international locations.
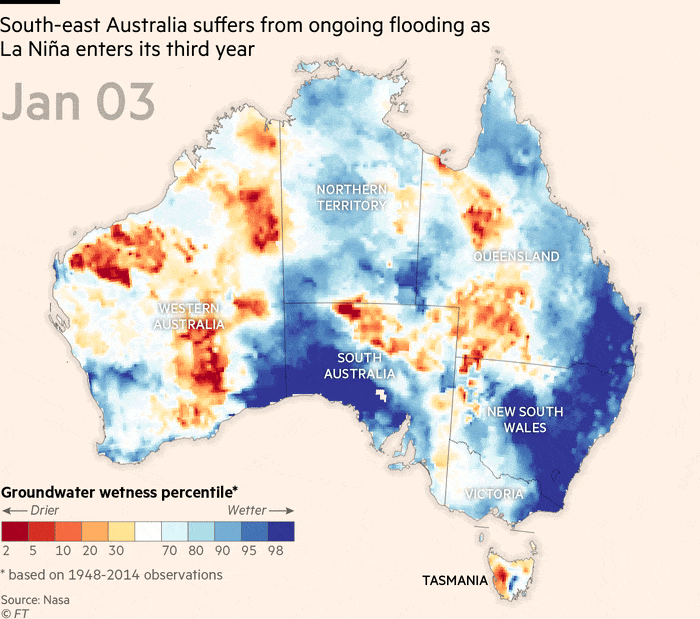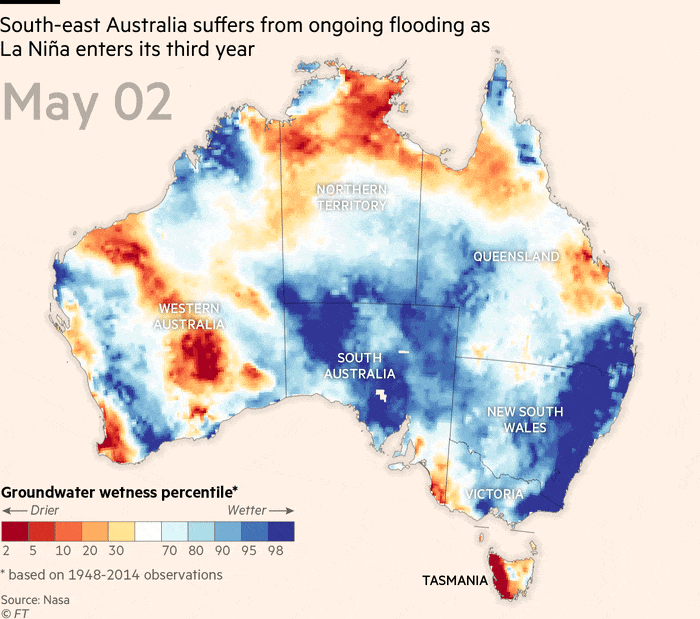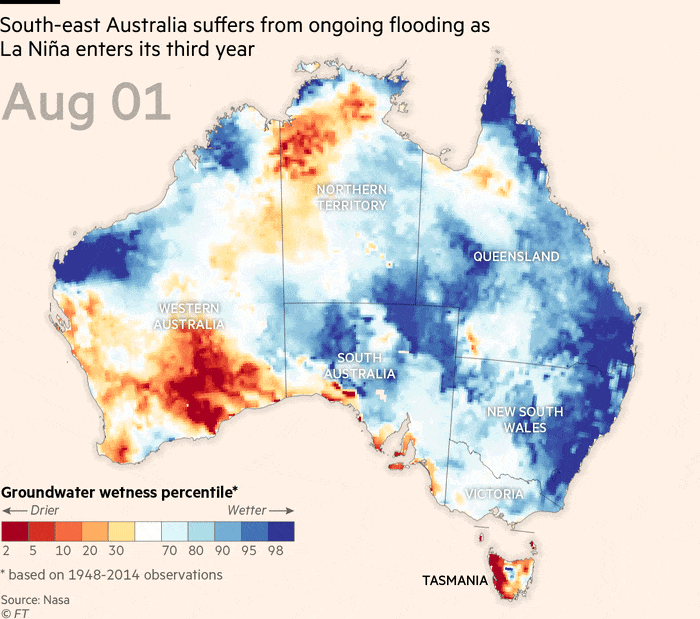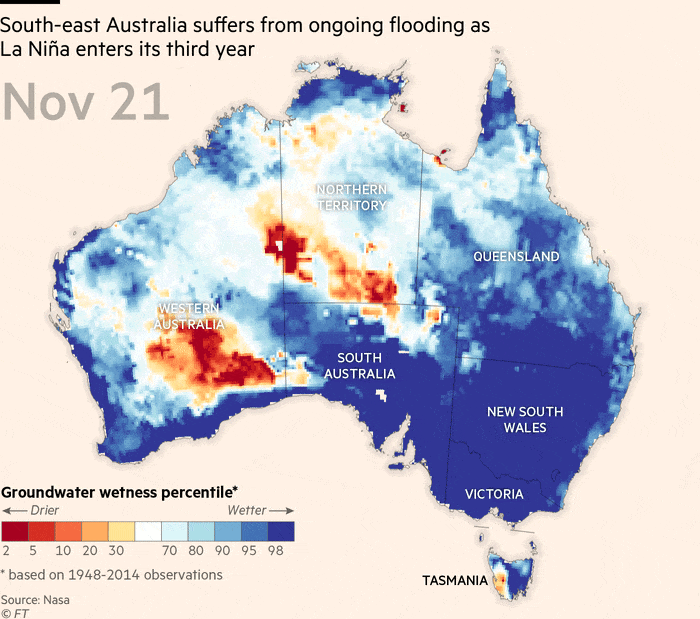
Throughout La Niña occasions over the previous two years, japanese Australia has skilled considered one of its most important flood intervals ever noticed, stated the nation’s Bureau of Meteorology and nationwide science company CSIRO in a State of the Local weather report this week.
The continent was now 1.47C hotter than in 1910, and sea ranges across the coast had been rising at an accelerating fee, stated the report.
Heavy rainfall occasions had develop into extra intense and the variety of short-duration heavy rainfall occasions was anticipated to extend. Longer fireplace seasons had been additionally anticipated in future.
Over the previous two years, the identical climate sample has additionally contributed to extreme drought in components of Africa, together with famine-struck Somalia.
Through the El Niño phenomenon, which reverses these traits, floor winds throughout the Pacific weaken, ocean temperatures within the central and japanese tropical Pacific are above common and there tends to be greater than common rainfall over the central or japanese Pacific.
Scientists check with a sample the place temperatures, winds and rainfall throughout the Pacific are at near-term averages as “Enso impartial”.
World temperatures have already risen by a minimum of 1.1C since pre-industrial occasions.
Michael McPhaden, a senior scientist with the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration within the US and one of many authors of the paper, stated “stronger” El Niños could be detected earlier than La Niñas as a result of the actual amplifying suggestions interactions between warming sea temperatures and weakening winds had been “extra vigorous”.
“A smaller hotter sea floor temperature will result in a bigger wind change, which is able to then result in a fair bigger sea floor change,” stated McPhaden.
He stated droughts in locations such because the western US had been partly amplified by Enso results.
Western US states have been gripped by a so-called “megadrought” for a lot of the 12 months, driving water ranges on the two largest reservoirs to report lows.
Earlier this 12 months, US authorities local weather scientists stated greater than half the nation was enduring drought situations. A separate research estimated that the drought affecting southwestern states was the worst to hit the area for 1,200 years after being exacerbated by human exercise.
McPhaden stated stronger variations of each La Niña and El Niño would possible amplify the present results of each climate patterns.
“The larger the sign within the tropical Pacific, the larger what we name teleconnections — the worldwide attain of El Niño, and it’ll are usually greater for giant occasions,” stated McPhaden.
“So the expectation is that if we now have stronger El Niños, we’re going to see these patterns which have repeated traditionally — from drought or flooding or wildfire or different extremes within the local weather system — we must always see these amplified in some sense.”
Local weather Capital

The place local weather change meets enterprise, markets and politics. Discover the FT’s protection right here.
Are you interested by the FT’s environmental sustainability commitments? Discover out extra about our science-based targets right here
Source link

