Brussels warns of EU recession as German output slides
[ad_1]
A steep drop in German output will assist drag the EU into recession this winter, as larger inflation and the Ukraine battle take a heavy toll on the bloc’s economic system, the European Fee has predicted.
Output throughout the union will contract within the present quarter and the primary three months of 2023, with Germany struggling one of many greatest falls in exercise as surging vitality prices curtail family spending energy and pressure factories to curb manufacturing.
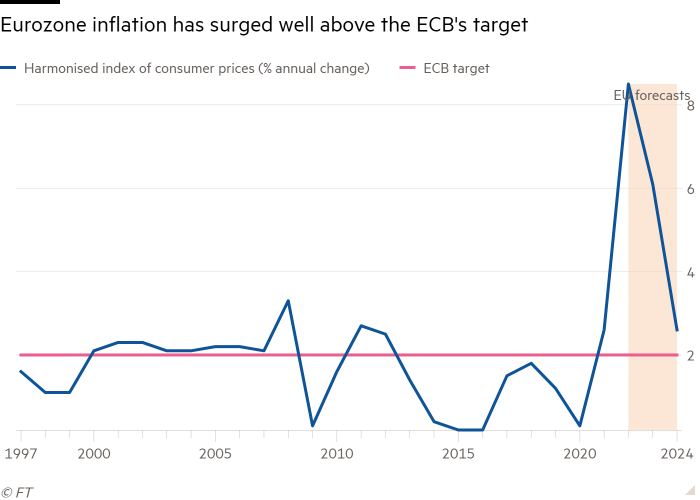
Inflation within the EU shall be larger than the fee forecast in the summertime, operating at 7 per cent over the course of 2023, down solely modestly from this yr’s anticipated 9.3 per cent.
The predictions add as much as a grim interval for the EU’s economic system, which had bounced again following the worst of the pandemic earlier than the Russian invasion of Ukraine and ensuing vitality value disaster. Germany, the union’s largest economic system, has been significantly hard-hit due to the significance of its energy-intensive business.
“The shocks unleashed by Russia’s battle of aggression in opposition to Ukraine are denting world demand and reinforcing world inflationary pressures,” the fee mentioned. “The EU is among the many most uncovered superior economies, as a consequence of its geographical proximity to the battle and heavy reliance on fuel imports from Russia.”
Output progress within the 27-member EU will decelerate to only 0.3 per cent in 2023, far under a previous forecast of 1.5 per cent printed this summer time, the fee projections confirmed. Germany is heading in the right direction for a 0.6 per cent full-year decline in actual gross home product in 2023, in accordance with the outlook, the worst efficiency within the euro space.
Whereas EU output progress is predicted to stay constructive over the present yr, at 3.3 per cent, the economic system will start contracting within the ultimate three months of the yr, shrinking 0.5 per cent, earlier than declining by an additional 0.1 per cent throughout the first quarter of 2023.
However, speedy value progress will most likely depart the European Central Financial institution heading in the right direction for additional financial tightening with an additional price rise to at the least 2 per cent predicted at its subsequent assembly in December.
The fee raised its forecast for eurozone inflation to eight.5 per cent this yr, 6.1 per cent subsequent yr and a couple of.6 per cent in 2024, in accordance with the figures. That compares with its July forecast for inflation within the bloc to fall from 7.6 per cent this yr to 4 per cent subsequent yr.
The ECB is because of publish its personal forecasts subsequent month, which can play a major position in figuring out the tempo and extent of future rate of interest rises. The central financial institution has already lifted its deposit price from minus 0.5 per cent to 1.5 per cent since July.
Traders shall be awaiting indicators that inflation may quickly peak within the eurozone, after shopper costs slowed within the US in October, in accordance with information launched on Thursday. This prompted a surge in fairness and bond markets as markets guess the US Federal Reserve would cease elevating charges sooner than beforehand anticipated.
A number of senior ECB policymakers have mentioned in current days {that a} gentle recession is not going to be sufficient to carry inflation again to its 2 per cent goal by itself and due to this fact it might want to increase charges above the purpose at which it restricts progress and inflicts ache on the labour market.
“There’s no time for financial coverage to pause,” mentioned Isabel Schnabel, an ECB government board member, on Thursday. “We might want to increase charges additional, most likely into restrictive territory, to carry inflation again to our medium-term goal in a well timed method.”
The fee expects the economic system to realize some traction by 2024, increasing by 1.6 per cent within the EU and 1.5 per cent within the euro space. But it surely warned the outlook was surrounded by an “distinctive diploma of uncertainty” due to the battle, with the most important risk stemming from the danger of vitality shortages within the winter of 2023-24.
“The EU economic system has proven nice resilience to the shockwaves this has prompted,” mentioned Paolo Gentiloni, economics commissioner. “But hovering vitality costs and rampant inflation at the moment are taking their toll and we face a really difficult interval each socially and economically.”
Source link

